

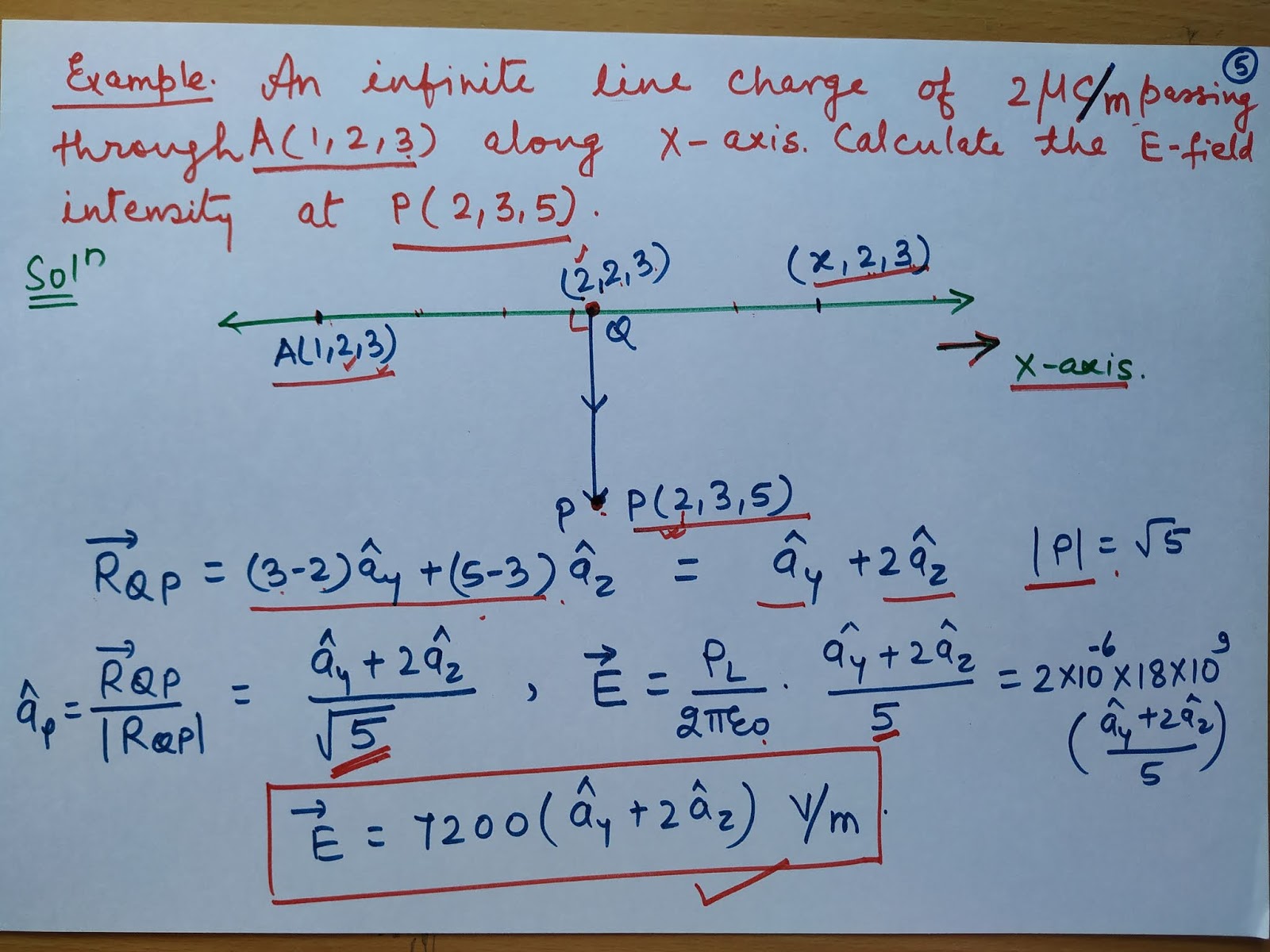
So, SI unit of electric field Intensity is N/C. We know that the SI unit of force is Newton (N) and the SI unit of charge is Coulomb (C). In that case the charges on the conductors will be Q 1 ' and Q 2’ respectively, where Q 1 + Q 2 = Q 1‘ + Q 2’. One can find the unit of electric field intensity from the equation, F q E or, E F /q. This condition, however, does not hold true if the conductors are of different sizes or of different material. Read from Lesson 4 of the Static Electricity chapter at The Physics Classroom. Electric field intensity at a point in between two parallel sheets with like charges of same surface charge densities () is 14. the force a proton would experience there. And law of conservation of charge is justified.Īs a consequence of conservation of charge, when two charged conductors of same size and same material carrying charges Q 1 and Q 2 respectively are brought in contact and separated, the charge on each conductor will be Q 1 + Q 2 2. The electric field intensity at a point in a vacuum is equal to: 1. Determine the electric field intensity at that point. For example, if we had an electric field vector which extended 1 unit in the x direction and 1 unit in the y direction, then its magnitude would be 1 2 + 1 2 2 units. The electric field intensity is the magnitude of the vector. A force of 5 N is acting on the charge 6 C at any point. The electric field is a vector, a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. Thus, the system of glass rod and silk cloth, which was neutral before rubbing, still possesses no net charge after rubbing. If the voltage V is supplied across the given distance r, then the electric field formula is given as. Hence, the total sum of charge on two bodies is zero. Since, the measure of charge is same on both, equal amount of charge with opposite nature will cancel out each other. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk cloth, glass rod becomes positively charged while silk cloth becomes negatively charged and, the amount of positive charge on the glass rod is apparently found to be exactly the same as the negative charge on silk cloth. Electric field intensity is independent of frequency, receiving antenna gain. True electric field strength is always expressed in some relative value of volts/meter - never in volts or milliwatts. Similarly, if there is a single negative charge then electric field lines start from infinity and end at a negative charge.Law of conservation of charge states that total charge on an isolated system of objects always remain conserved. The electric field intensity unit dBu is the unit used extensively by the Federal Communications Commission when referring to field strength. Electric field lines start from positive charges and end at negative charges. If there is a single positive charge then electric field lines start from positive charge and end at infinity.Electric field lines are drawn to represent the electric field. Electric field intensity within the dielectric cylinder will, therefore, have only the x-component, which is given by Exi-Vix-2ee+iE0(10.68).An electric field line is an imaginary line along which a positive test charge will move if left free.The electric field strength is dependent upon the quantity of charge on the source charge ( Q) and the distance of separation ( d) from the source charge. Therefore the direction of the electric field intensity at a point due to an infinitely long straight uniformly positive charged wire will be radially outward. The new formula for electric field strength (shown inside the box) expresses the field strength in terms of the two variables that affect it.) of the individual charges: E E 1 + E 2 + E 3 +. Electric field lines start from positive charges and end at negative charges. If there is a single positive charge then electric field lines start from positive charge and end at infinity. The intensity of an electric field satisfies the principle of superposition, according to which for a given point in space, the intensity of the field E, created by several charges, is equal to the sum of the field intensities (E 1, E 2, E 3.The direction of the electric field at every point must be radial (outward if λ > 0, inward if λ 0, inward if λ Where E = electric field intensity, q o = charge on the particleĮlectric field intensity due to an infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire: It is defined as the force experienced by a unit positive test charge in the electric field at any point. Electric field strength is a quantitative expression of the intensity of an electric field at a particular location.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
